In the hidden corners of our planet, beneath the layers of soil and intertwined with the roots of plants, lies an astonishing world that often goes unnoticed. This world is home to some of nature’s most intricate and mesmerizing creations: the fungal root web shapes. These delicate, yet robust structures not only play a crucial role in the ecosystem but also captivate those who dare to delve into their enigmatic beauty. Fungi, often overshadowed by their more charismatic plant and animal counterparts, hold the secrets to a complex subterranean network that is as vital as it is visually arresting. 🌿🍄
Imagine walking through a dense forest, the sunlight filtering softly through the canopy, your feet cushioned by the rich, loamy earth. Beneath this serene surface, an elaborate network of fungal threads, known as mycorrhizae, stretches out in a complex lattice, connecting roots and facilitating a symbiotic dance of life. This unseen web is not only a testament to the complexity of nature but also a cornerstone in the survival and health of countless plant species. By exploring these fungal root networks, we can unlock new insights into ecological balance, biodiversity, and even potential agricultural innovations.
In this exploration of fungal root web shapes, we will journey into the heart of these natural masterpieces. We’ll examine the science behind mycorrhizal networks, delving into their formation, structure, and the critical roles they play in plant health and soil ecosystems. From the intricate patterns of mycelial growth to the surprising ways in which these networks enhance nutrient exchange and water absorption, the fungal root web is a marvel of natural engineering. Understanding these networks not only enriches our appreciation of the natural world but also offers promising pathways for sustainable agricultural practices.
Moreover, we’ll consider the cultural and historical significance of fungi, from ancient lore to modern scientific breakthroughs. Fungi have long been revered and utilized in various cultures, often associated with mysticism and healing. Today, they are at the forefront of scientific research, with mycorrhizal networks being studied for their potential applications in combating climate change and improving crop resilience. By examining these cultural narratives alongside cutting-edge research, we’ll uncover the profound impact fungi have had on human societies and their potential to shape our future.
Join us on this captivating journey into the world beneath our feet, where the intricate beauty of fungal root web shapes awaits discovery. This exploration promises to illuminate the unseen connections that sustain life on Earth and inspire a deeper appreciation for the hidden wonders of nature. Whether you’re a seasoned botanist, a curious nature enthusiast, or someone simply intrigued by the mysteries of the natural world, this deep dive into the fungal realm is sure to enrich your understanding and ignite your imagination. Let’s unearth the secrets of these subterranean artists and celebrate the extraordinary beauty they bring to our world. 🍂🔍
The Hidden Complexity of Fungal Root Web Shapes
Fungi, often relegated to the role of decomposers in nature’s grand cycle, hold secrets far more profound and intricate than many of us realize. The underground networks they form, often in symbiosis with plant roots, are a testament to the complexity and beauty of natural systems. These fungal root webs, known scientifically as mycorrhizal networks, serve as vital conduits for nutrients, water, and information between plants, fostering an interconnectedness that supports entire ecosystems. Their intricate structures, which can span vast distances, are a testament to nature’s ingenuity.
These webs, while hidden from view, play a crucial role in the survival of many plant species. The symbiotic relationship between fungi and plants is not merely a matter of nutrient exchange; it is a dynamic interaction that influences plant health, resilience, and even their evolutionary trajectories. Fungi enhance the plant’s access to nutrients by extending their root systems with thin, thread-like structures called hyphae. This expansion allows plants to access water and nutrients far beyond their root zones, significantly boosting their growth and survival chances.
Moreover, fungal networks have been shown to facilitate communication between plants. When a plant is under threat, it can send distress signals through these networks, alerting neighboring plants to prepare their defenses. This fascinating phenomenon, often referred to as the “Wood Wide Web,” underscores the complexity and sophistication of these underground systems. Despite their importance, mycorrhizal networks remain largely unexplored, with many of their mysteries still to be uncovered by scientists.
Fungal Networks: A Vital Component of Ecosystem Health
The ecological significance of mycorrhizal networks cannot be overstated. These networks are essential for maintaining the health and stability of ecosystems, particularly in nutrient-poor environments. By facilitating nutrient exchange, they enhance plant growth and biodiversity, which in turn supports a wide range of animal species. Furthermore, mycorrhizal networks contribute to soil health by improving soil structure, enhancing water retention, and reducing erosion.
The impact of these networks extends beyond individual ecosystems. They play a crucial role in global carbon cycling by sequestering carbon in the soil. This process helps mitigate climate change by reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. However, the disruption of these networks due to human activities, such as deforestation and soil degradation, poses a significant threat to their functioning and the ecosystem services they provide.
Understanding and preserving these networks is therefore of paramount importance. Conservation efforts should prioritize maintaining the integrity of mycorrhizal networks to ensure the continued health and resilience of ecosystems. Scientists are increasingly recognizing the need to study these networks in greater detail to fully appreciate their complexity and the myriad benefits they offer.
Exploring the Diversity of Fungal Root Web Structures
Fungal root web structures exhibit a remarkable diversity that reflects the variety of ecological niches they occupy. Different fungi form different types of mycorrhizal associations, each with its own unique characteristics and functions. The two main types of mycorrhizal associations are ectomycorrhizal and arbuscular mycorrhizal, both of which play distinct roles in plant-fungal interactions.
Ectomycorrhizal fungi form a dense network of hyphae around the outside of plant roots, creating a sheath that facilitates nutrient exchange. These fungi are particularly common in temperate and boreal forests, where they associate with many tree species, such as pines, oaks, and birches. In contrast, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi penetrate the root cells of plants, forming intricate structures known as arbuscules. These fungi are more prevalent in grasslands, tropical forests, and agricultural systems.
The diversity of fungal root web structures is a reflection of the evolutionary adaptability of fungi. By forming different types of associations, fungi can exploit a wide range of ecological niches and contribute to the functioning of diverse ecosystems. This adaptability is one of the reasons why mycorrhizal networks are so successful in colonizing various habitats around the world.
Comparative Analysis of Mycorrhizal Networks
To appreciate the complexity of mycorrhizal networks, it is essential to compare their structures, functions, and ecological roles. The table below highlights some of the key differences between ectomycorrhizal and arbuscular mycorrhizal networks.
| Characteristic | Ectomycorrhizal Networks | Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Networks |
|---|---|---|
| Root Association | External sheath around roots | Penetrate root cells |
| Common Plant Hosts | Trees in temperate/boreal forests | Plants in grasslands/tropical forests |
| Ecological Role | Enhance nutrient absorption | Boost plant resistance to stress |
| Geographical Distribution | Temperate and boreal regions | Global, with high prevalence in tropics |
Each type of mycorrhizal network has adapted to specific environmental conditions, making them highly effective in supporting plant growth and ecosystem stability. By understanding these differences, we can better appreciate the role of fungi in nature and the importance of preserving their habitats.
The Role of Mycorrhizal Networks in Agricultural Systems
Mycorrhizal networks are not only vital for natural ecosystems but also have significant implications for agriculture. These networks can enhance crop productivity by improving nutrient uptake, particularly phosphorus, which is often a limiting factor in agricultural soils. By forming symbiotic relationships with crops, mycorrhizal fungi can increase yield and reduce the need for chemical fertilizers.
The benefits of mycorrhizal networks extend beyond nutrient uptake. They also improve soil structure, increase water retention, and reduce erosion, leading to more sustainable agricultural practices. By promoting plant health and resilience, these networks can help mitigate the impacts of environmental stressors, such as drought and soil degradation, which are becoming increasingly prevalent due to climate change.
Incorporating mycorrhizal networks into agricultural systems represents a promising strategy for achieving sustainable food production. However, this requires a shift in traditional agricultural practices to prioritize soil health and biodiversity. Farmers and researchers must work together to develop innovative techniques that harness the power of mycorrhizal networks while minimizing their disruption.
Fostering Awareness and Research on Fungal Networks
Despite their ecological importance, mycorrhizal networks remain largely underappreciated and understudied. Raising awareness about the role of these networks is crucial for their conservation and the continued health of ecosystems. Educating the public about the benefits of mycorrhizal networks can inspire more sustainable practices and foster greater appreciation for the natural world.
Research on mycorrhizal networks is also essential for uncovering their full potential. Scientists are continually discovering new aspects of these networks, such as their ability to store and transfer carbon, communicate between plants, and adapt to changing environmental conditions. This research can inform conservation efforts and guide policies that protect these vital systems.
Engaging in citizen science projects and community outreach programs can help bridge the gap between scientific research and public understanding. By involving communities in the study and preservation of mycorrhizal networks, we can foster a deeper connection with nature and promote a more sustainable future.
For a deeper understanding of the fascinating world of mycorrhizal networks, we recommend watching the following video: “The World of Mycorrhizal Networks” by Nature’s Great Wonders.
- Explore how mycorrhizal networks influence plant communication.
- Learn about the diverse types of fungal associations with plants.
- Discover the impact of mycorrhizal networks on agriculture and sustainability.
In summary, mycorrhizal networks are a hidden yet essential component of Earth’s ecosystems. By unveiling their intricate beauty and understanding their roles, we can better appreciate the interconnectedness of nature and the importance of preserving these hidden masterpieces.
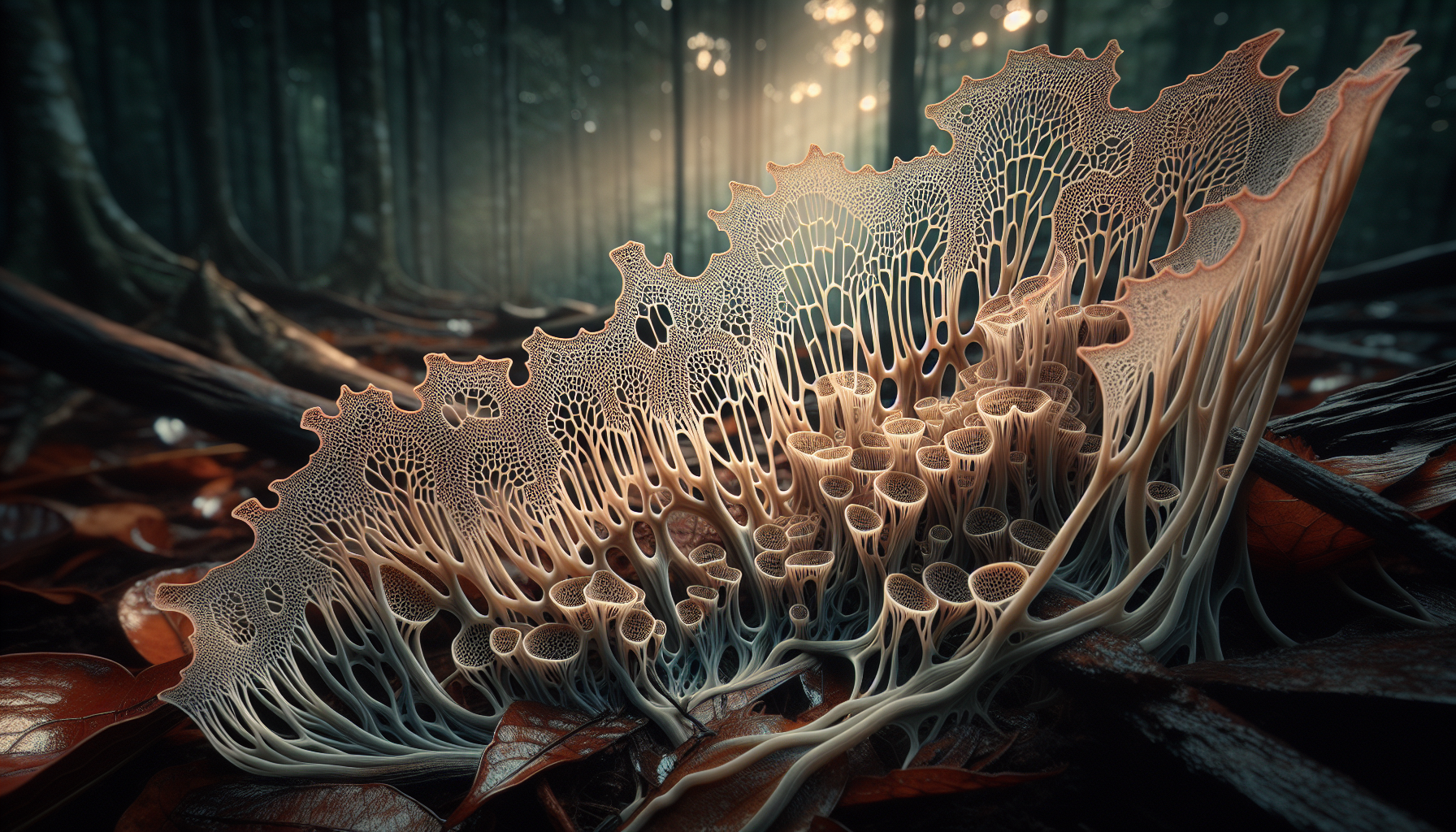

Conclusion
Unveiling the intricate beauty of fungal root web shapes has been an enlightening journey into the hidden masterpieces of nature. Throughout this article, we have explored the complex and mesmerizing structures of fungal root webs, delving into their ecological significance and the aesthetic allure they present. These subterranean networks, often unnoticed by the untrained eye, play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance, facilitating nutrient exchange, and supporting plant health. By examining the unique morphology and adaptive strategies of these fungal networks, we have gained a deeper appreciation for their essential functions and the lessons they impart about interconnectedness in nature.
The article began by setting the stage with an introduction to the symbiotic relationship between fungi and plant roots, known as mycorrhizal associations. These associations are fundamental to the growth and survival of most terrestrial plants, providing them with increased access to water and nutrients in exchange for carbohydrates. We highlighted the various types of mycorrhizal associations, including ectomycorrhizal and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, each with distinct characteristics and roles within the ecosystem. The diversity of these relationships underscores the adaptability and evolutionary success of fungi, as well as their integral role in supporting biodiversity.
As we ventured further into the article, we explored the aesthetic and structural complexity of fungal root webs. The intricate patterns formed by these networks are not only functional but also exhibit a natural beauty that has inspired artists and scientists alike. The fractal-like structures of mycorrhizal networks demonstrate nature’s penchant for efficiency and optimization, optimizing nutrient absorption and distribution across vast distances. The remarkable architecture of these webs serves as a testament to the ingenuity of evolutionary processes and the subtle artistry inherent in the natural world.
The ecological significance of fungal root webs cannot be overstated. These networks enhance soil structure, improve water retention, and increase resilience against environmental stressors, such as drought and pathogens. By facilitating nutrient cycling and promoting plant diversity, mycorrhizal fungi contribute to the stability and productivity of ecosystems. Furthermore, they play a pivotal role in carbon sequestration, helping mitigate the impacts of climate change by storing carbon in the soil. Understanding and preserving these vital networks is essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems and supporting global efforts to combat environmental degradation.
In addition to their ecological importance, fungal root webs offer valuable insights for scientific research and innovation. The study of mycorrhizal networks has led to breakthroughs in agriculture, forestry, and environmental restoration. By harnessing the natural abilities of fungi, researchers and practitioners can develop sustainable agricultural practices, improve crop yields, and restore degraded landscapes. The potential applications of mycorrhizal fungi extend to biotechnology, where their unique enzymes and metabolic pathways are explored for industrial and medical purposes. The versatility and resilience of these networks inspire continued exploration and discovery in various scientific fields.
Throughout this article, we have emphasized the interconnectedness and interdependence of all living organisms within ecosystems. Fungal root webs exemplify the delicate balance of nature, where every component plays a role in sustaining the whole. As we gain a deeper understanding of these intricate networks, we are reminded of the importance of preserving and protecting our natural environment. The beauty and complexity of fungal root webs invite us to appreciate the wonders of the natural world and to recognize our responsibility in safeguarding it for future generations.
In conclusion, unveiling the beauty and significance of fungal root web shapes has been a profound exploration of nature’s hidden masterpieces. These networks, often overlooked, hold the key to understanding ecosystem dynamics and offer promising solutions for sustainable development and environmental conservation. We encourage you, our readers, to reflect on the insights gained from this article and consider the broader implications of mycorrhizal networks in your own lives and communities. Whether you are a scientist, an artist, an environmentalist, or simply a curious mind, there is much to learn and appreciate in the world of fungi.
Share your thoughts and experiences with us in the comments below. Let’s foster a community of curiosity and appreciation for the natural world. Feel free to share this article with others who may find inspiration in the remarkable world of fungal root webs. Together, we can continue to explore, understand, and protect the intricate beauty of our planet 🌍.
For further reading and to stay updated with ongoing research, you can explore resources from institutions such as the Mycological Society of America (http://msafungi.org/) and the Global Mycorrhizal Network (http://mycorrhizas.info/), which provide valuable insights into the latest advancements in mycorrhizal research. Let’s celebrate and preserve the hidden masterpieces that nature has crafted, one fungal root web at a time. 🌱
Toni Santos is a visual explorer and microscopic storyteller who delves into the hidden aesthetics of microbial life. Through a fusion of scientific curiosity and artistic insight, Toni transforms the overlooked world of bacteria, fungi, and cellular forms into mesmerizing visual narratives—revealing the elegance, symmetry, and chaos that thrive at microscopic scales.
Rooted in a fascination with life forms too small to see yet too intricate to ignore, Toni’s work captures the bizarre beauty of microbial colonies, biofilms, and spore patterns. These images aren’t just representations—they are celebrations of the artistic intelligence encoded in nature’s tiniest architects.
With a background in visual design and bio-inspiration, Toni merges scientific imaging techniques with creative expression, transforming petri dish cultures, fluorescence microscopy, and microbial textures into works that provoke both wonder and contemplation.
As the creative force behind Vizovex, Toni offers curated visual studies, microbial-inspired designs, and essays that bridge art and microbiology—inviting viewers to reimagine what beauty means at the edge of perception.
His work is a tribute to:
The hidden geometries of living systems
The surprising elegance of microbial growth
The role of micro-life in shaping visual culture
Whether you’re a scientist, artist, or simply curious about the unseen world that sustains us, Toni opens a window into a universe where life writes poetry in colonies and patterns, one microbe, one frame, one breathtaking detail at a time.